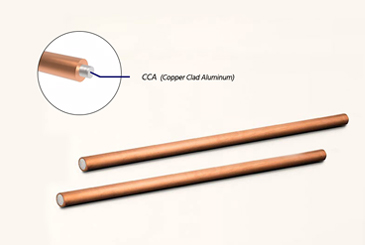
Copper-clad aluminum CCA wire refers to a new conductor material formed by coating a thin copper layer on the aluminum core wire and making the atomic bonds on the interface between copper and aluminum produce metallurgical bonding.
It not only takes advantage of the excellent electrical conductivity of copper and the light weight of aluminum, but also overcomes the disadvantages of easy oxidation of aluminum, high contact resistance, and difficult welding of joints, and greatly saves the scarce copper resources in my country and reduces the cost of conductors.
Mainly used in coaxial cable inner conductor, audio and video cable conductor, shielded braided soft conductor or enamelled winding wire base material, etc.
Why choose Chalco Aluminum's copper clad aluminum CCA wire?
Quality could full meet ASTM B566 2002 and SJ/T 11223-2000.
The preparation of high-quality copper-clad aluminum CCA wire blanks ensures the bondability of the copper-aluminum interface; the quality of copper strips and aluminum rods is ensured, and the copper ensures the high-quality drawability of copper-clad aluminum wires; through heat treatment of copper-clad aluminum wires, the The annealability of the copper-clad aluminum wire; the connection of the copper-clad aluminum wire is better, and the copper-clad aluminum wire has excellent weldability.
Specs of copper clad aluminum CCA wire
| Alloy | T2+1060 |
| Temper | Hard, Soft |
| Length | Coil |
| Standard | ASTM B566 2002, SJ/T 11223-2000 |
Types of copper clad aluminum CCA wire
Copper clad aluminum wires are divided into two grades of 10% and 15% according to the volume ratio of copper layer, divided into soft state (Annealed, Abbreviated as A) and hard state (Hard, Abbreviated as H), the model is CCA;
Copper-clad aluminum alloy wire is divided into three grades according to the copper layer volume ratio: 10%, 15% and 20%, all of which are soft (Annealed), and the model is CCAA;
Tinned copper-clad aluminum alloy wire is also divided into three grades of 10%, 15% and 20% according to the copper layer volume ratio, all of which are soft (Annealed), and the model is CCAAT.
Model, specification and wire diameter deviation
| Model | Diameter mm | Diameter tolerance mm |
| CCA (10A, 10H, 15A, 15H) | <0.300 | 0.003 |
| ≥0.030 | ±1%d | |
| CCAA ( 10A) | 0.150-0.200 | ±0.003 |
| 0.200-0.600 | ±0.005 | |
| CCAA(15A, 20A) | 0.080-0.200 | ±0.003 |
| 0.200-0.600 | ±0.005 | |
| CCAAT(10A) | 0.150-0.200 | ±0.003 |
| 0.200-0.600 | ±0.005 | |
| CCAAT (15A, 20A) | 0.080-0.200 | ±0.003 |
| 0.200-0.600 | ±0.005 |
Thickness and volume ratio
| Model | Type | The thinnest point | Volume ratio |
| CCA | 10A, 10H | ≥1.75%d | Not less than 8% and not more than 12% |
| 15A, 15H | ≥2.50%d | Not less than 13% and not more than 17% | |
| CCAA, CCAAT | 10A | ≥2.00%d | Not less than 10% and not more than 12% |
| 15A | ≥3.25%d | Not less than 15% and not more than 17% | |
| 20A | ≥4.50%d | Not less than 20% and not more than 22% |
Resistivity
| Model | Type | Maximum resistivity/(Ω*mm 2 /m) |
| CCA | 10A, 10H | 0.02743 |
| 15A, 15H | 0.02676 | |
| CCAA | 10A | 0.0279 |
| 15A | 0.027 | |
| 20A | 0.0262 | |
| CCAAT | 10A | 0.0284 |
| 15A | 0.0275 | |
| 20A | 0.0267 |
Mechanical properties of CCA
| Diameter/mm | Tensile strength/Mpa | Elongation/% | ||
| Category H (minimum) | Category A (Minimum) | Category H (minimum) | Category A (Minimum) | |
| 0.080-0.120 | 205 | 172 | 1.0 | 5 |
| 0.121-0.360 | 207 | 172 | 1.0 | 5 |
| 0.361-0.574 | 207 | 172 | 1.0 | 10 |
| 0.575-0.642 | 207 | 138 | 1.0 | 10 |
| 0.643-2.05 | 207 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 2.06-2.30 | 200 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 2.31-2.59 | 193 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 2.60-2.91 | 186 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 2.92-3.26 | 179 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 3.27-3.67 | 172 | 138 | 1.0 | 15 |
| 3.68-4.12 | 166 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 4.13-4.62 | 159 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 4.63-5.19 | 152 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 5.20-5.83 | 138 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 5.84-6.54 | 124 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 6.55-8.25 | 110 | 138 | 1.5 | 15 |
Mechanical properties of CCAA, CCAAT
| Model | Type | Diameter/mm | Tension Strength /Mpa | Elongation/% |
| CCAA, CCAAT | 10A, 15A, 20A | 0.080≤d≤0.100 | 185 | 9 |
| 0.100≤d≤0.200 | 180 | 10 | ||
| 0.200≤d≤0.400 | 175 | 12 | ||
| 0.400≤d≤0.600 | 170 | 13 |
Density of CCA, CCAA and CCAAT at 20℃
| Model | Type | Density /(gcm3) | Deviation |
| CCA | 10A, 10H | 3.3 | ±3% |
| 15A, 15H | 3.63 | ±3% | |
| CCAA, CCAAT | 10A | 3.32 | 0-0.13 |
| 15A | 3.63 | 0-0.13 | |
| 20A | 3.94 | 0-0.13 |
Features of copper clad aluminum CCA wire
Lightweight: The core of copper-clad aluminum wire is aluminum, which is lighter than pure copper wire. This makes copper-clad aluminum wire an advantage in applications where overall weight reduction is required, such as in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Low cost: Due to the relatively low price of aluminum, the cost of copper-clad aluminum wire is lower than that of pure copper wire. This makes copper-clad aluminum wire an economical choice, especially for applications where large quantities of wire are used, such as construction, power transmission, and communications.
Electrical conductivity: Copper-clad aluminum wire has a certain difference in electrical conductivity compared to pure copper wire. Due to the lower electrical conductivity of aluminum, the resistance of copper clad aluminum wire will be slightly higher than that of pure copper wire of the same size. Therefore, in some applications that require high electrical conductivity, the limitations of copper-clad aluminum wires may need to be considered.
Corrosion resistance: The copper cladding of the copper clad aluminum wire provides good corrosion resistance and can resist some common corrosive media. This makes copper clad aluminum wire more reliable in some specific environments, such as outdoors and humid environments.
Machinability: Copper-clad aluminum wire has good machinability and can be cut, stripped and connected using conventional wire processing techniques. This makes copper clad aluminum wire easy to install and maintain.
Although copper-clad aluminum wire has some advantages, the selection of copper-clad aluminum wire should be evaluated according to the requirements and limitations of specific applications. For some demanding applications, such as high current loads or applications requiring lower resistance, it may be necessary to use pure copper wire.
Uses of copper clad aluminum CCA wire
Power transmission: Copper-clad aluminum wire can be used to transmit power, including low-voltage and medium-voltage power transmission systems. They can be used in electrical wiring of buildings, power distribution networks, and for industrial and commercial purposes.
Communication systems: Copper-clad aluminum CCA wires are often used in telephone lines, network cables, and other communication systems. They provide reliable signal tranmission and data transmission capabilities.
Automotive industry: Copper-clad aluminum wires are widely used in automotive electrical systems. They are used in the manufacture of wires and cables for vehicles, such as battery wires, engine wiring harnesses, light circuits, etc.
Electronic equipment: Copper-clad aluminum wire can be used for internal wiring and connection of electronic equipment. They are widely used in televisions, audio equipment, computers and other consumer electronics.
Aerospace: Copper-clad aluminum wires have important applications in aerospace due to their lightweight properties. Copper-clad aluminum wire can be used in aircraft electrical systems, communication equipment, and internal connections of spacecraft.
It should be noted that the specific application depends on the specification of the copper clad aluminum wire, the current capacity requirement, and the technical requirements of the specific project. When selecting and using copper-clad aluminum wire, it should be evaluated and confirmed according to the application environment and relevant standards.

Precautions for purchasing copper clad aluminum CCA wire
Application requirements: determine the specifications and characteristics of the copper-clad aluminum wire you need. Consider the wire's current capacity, electrical resistance, insulation material, heat resistance, and more to ensure it meets your application needs.
Standards and certification: make sure that the purchased copper clad aluminum wire meets the relevant standards and certification requirements. These standards can be international standards (such as IEC, ASTM) or industry specifications. Verify that suppliers provide products that meet quality requirements.
Supplier reputation: choose a reputable supplier or distributor to purchase copper clad aluminum wire. The reliability of suppliers can be evaluated by referring to customer evaluations, industry reputation and supplier qualification certification.
Quality control: understand the supplier's quality control measures and production process. Ask the supplier if they have rigorous quality checks and make sure the product meets the relevant quality standards.
Price and cost-effectiveness: compare the prices and product quality of different suppliers to ensure that you are getting copper clad aluminum wire at a reasonable price and cost-effectiveness. Consider the balance between price, performance and reliability.
Applicable standards and regulations: make sure that the copper-clad aluminum wire you purchase complies with applicable standards and regulatory requirements, especially those pertaining to wire and cables in a particular industry or region.
After-sales service: learn about the after-sales service and technical support provided by the supplier. Make sure you have access to the necessary support and avenues to resolve issues after your purchase.
To sum up, when purchasing copper-clad aluminum wire, it is necessary to comprehensively consider application requirements, product quality, supplier reliability, and compliance with standards and regulations. Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure you get the products and support you expect.