Aluminum Brazing refers to the use of filler materials (called brazing materials) with a melting point lower than that of the base metal (brazed material), and the filling material is melted at a temperature lower than the melting point of the base metal and higher than the melting point of the brazing material. It is a welding method in which the material wets and spreads on the surface of the base material and fills the gap in the base material, and dissolves and diffuses with the base material to realize the connection between the parts.
This article mainly introduces the aluminum alloy brazing process, brazing methods, and aluminum alloy brazing materials. If you have any doubts about brazing or any requirements related to aluminum alloy brazing, feel free to contact Chalco for support.Welcome contact
How does the brazing process work?
The brazing process is related to the comprehensive action of reduction and decomposition in solid phase, liquid phase and gas phase, as well as physical and chemical phenomena such as wetting and capillary flow, diffusion and dissolution, solidification and adsorption, evaporation and sublimation.
Brazing can be divided into three basic processes:
- The first is the melting and filling process of the flux, that is, the pre-set flux flows into the gap of the base metal after heating and melting, and has a physical and chemical interaction with the oxide on the surface of the base metal to remove the oxide film, clean the surface of the base metal, and become a brazing material, creating conditions for filler metal caulking.
- The second is the process of melting the solder and filling the solder joint, that is, as the heating temperature continues to rise, the solder begins to melt, wet and spread, and remove the residue of the solder.
- The third is the interaction process between the solder and the base metal, that is, under the action of the molten solder, a small part of the base metal dissolves in the solder (that is, the diffusion of the base metal to the liquid solder), and the solder diffuses into the base metal , some complex chemical reactions will also occur at the solid-liquid interface. When the solder fills the gap and keeps it warm for a certain period of time, it begins to cool and solidify to form a brazed joint.

Methods of aluminum brazing process
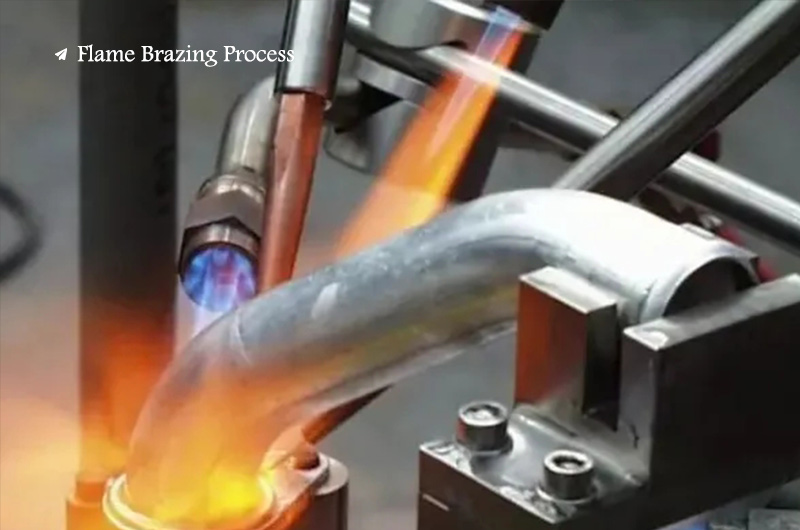
Flame brazing process
The heatsource is an oxygen gas flame, and there are many types of gas. For aluminum and its alloys, the applicable gas includes acetylene and natural gas. Flame brazing of aluminum and its alloys must be accompanied by flux. Since there is no color change in the aluminum heating process, it is difficult to grasp the brazing heating temperature during flame brazing.


Dip brazing aluminum process
Immerse parts in molten flux for fast, non-oxidizing brazing, ideal for high-quality, productive mass production. Post-brazing cleanup is essential to prevent corrosion and environmental pollution.
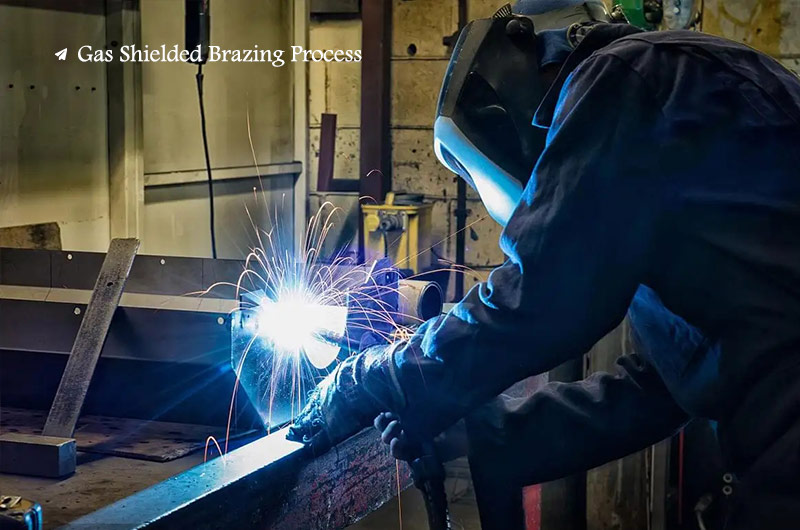
Gas shielded brazing process
Inert gas protection is used, the connection surface needs to be thoroughly cleaned before brazing, the atmosphere in the furnace needs to be replaced and then fed continuously, and the production cost is high. If nitrogen protection is used, non-corrosive flux must be used. This method has high productivity and has been widely used.
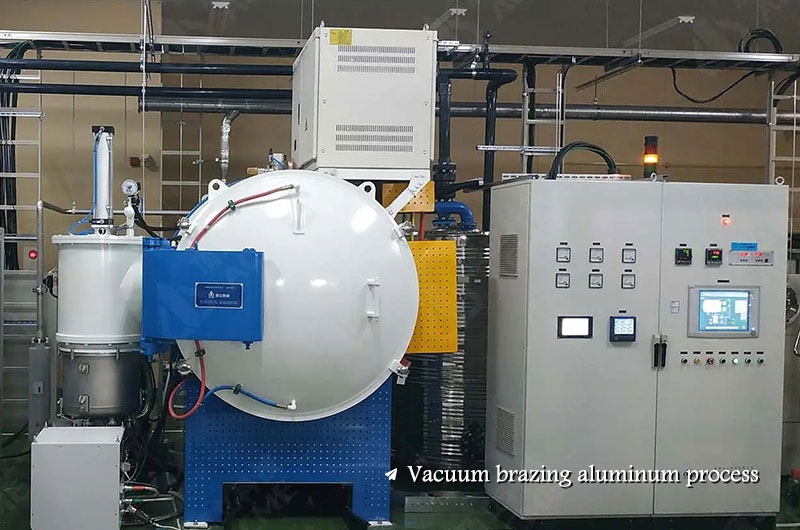


Vacuum brazing aluminum process
Furnace brazing method without the use of flux. The vacuum degree shall not be lower than 1.33X10 -2Pa. The use of metal magnesium as an activator and other technological measures has made the vacuum brazing technology of aluminum and its alloys popularized and applied.
Aluminum brazing material
Clad aluminum brazing welding material
Clad aluminum brazing material blends aluminum-manganese core for strength and heat dissipation with aluminum-silicon cladding for better weldability. Commonly in forms like plates, strips, or foils, it's widely applied across diverse fields.
Contact us now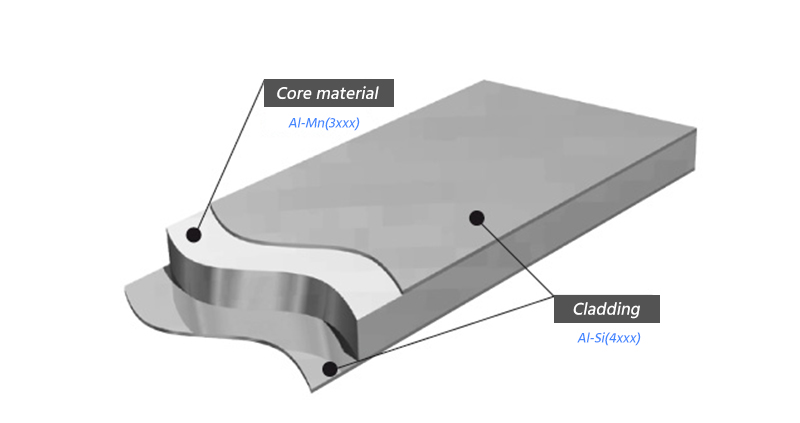
The characteristics of brazing aluminum sheet foil coil strip
- The Aluminum Cladding Fin and Sheet have advantages of compact structure, high heat dissipation efficiency, and good collapse resistance;
- Aluminum brazing composite materials have good wettability and flowability;
- Aluminum Brazing Fin and Sheet have good corrosion resistance;
- Clad aluminum brazing sheet has good machinability.
The application of brazing aluminum sheet foil coil strip
The brazing aluminum sheet foil coil strip are widely used in automotive heat exchange systems, such as engine radiators, engine oil radiator, medium refrigerator, air -conditioning condenser and evaporator etc.
Aluminum brazing filler
Aluminum Brazing Filler is usually used for brazing of aluminum and aluminum alloy, aluminum copper brazing, aluminum steel brazing, aluminum stainless steel brazing, etc.
Contact us now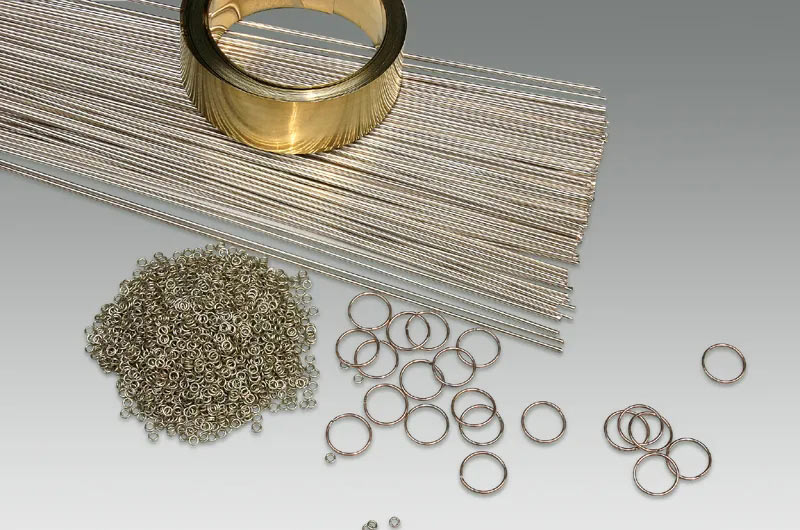
Brazing methods
flame aluminum brazing, induction aluminum brazing, aluminum brazing in atmosphere protection furnace, vacuum aluminum brazing, etc.
Material forms
welding wire, welding ring, welding ribbon, solder sheet, solder powder, solder paste (both non-corrosive flux and corrosive flux formulations) and custom pre-formed shapes.
At the same time, our company can also provide flux-cored wire or welding ring of aluminum-based brazing materials for aluminum welding and aluminum brazing.
Aluminum brazing flux
Physical state:white powder, particle size ≤250um, density: 1.3-1.4 g/cm3
Main ingredients:alkali metal and alkaline earth metal chlorides, fluorides, active agents.
Contact us now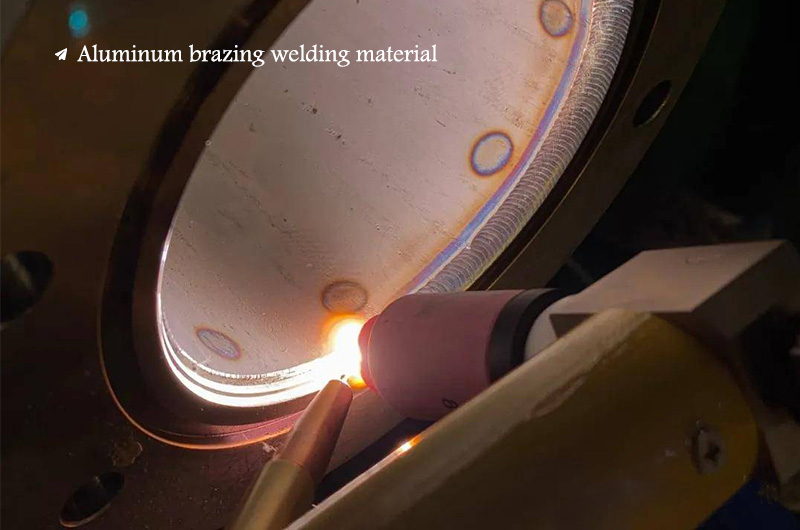
Product advantages
- Quickly and effectively remove the oxide film on the surface of aluminum parts and reduce the surface tension of the base metal;
- The powder particle size is moderate, not easy to settle;
- Flux and base metal have good wettability, good fluidity, and stable brazing quality;
- The composition of the flux is close to the eutectic point and the melting point is low;
- Comply with the environmental requirements of RoHS.
The scope of application of aluminum flux
Suitable for brazing of aluminum and aluminum alloy materials. It is suitable for brazing methods such as various gas shielded furnaces or low-temperature flames, brazing pure aluminum, aluminum-manganese and other alloys. Non-toxic, odorless, non-polluting, long-term storage without moisture absorption, non-caking.
The melting temperature of non-corrosive aluminum brazing flux is relatively narrow, and the temperature is about 550 ℃. Especially at present, it is the most ideal welding solvent for the welding of most automobile air conditioners, aluminum condensers and aluminum radiator furnaces.
The features of aluminum brazing
- The heating temperature of aluminum brazing is low, the joint is smooth and flat, the structure and mechanical properties change little, the deformation is small, and the workpiece size is accurate.
- It can weld the same metal or dissimilar materials, and there is no strict limit on the thickness difference of the workpiece.
- Some brazing methods can weld multiple weldments and joints at the same time, and the productivity is very high.
- The brazing equipment is simple, and the production investment cost is low.
- The strength of the joint is low, the heat resistance is poor, and the requirements for cleaning before welding are strict, and the price of the solder is relatively expensive.
Application fields of aluminum brazing
- Aluminum brazing is suitable for the welding of automotive air conditioners, intercoolers, condensers, evaporators, water tanks and various aluminum radiators;
- Welding of aluminum body frame structure, such as the connection between the top cover and the case wall, car doors and other products;
- Aluminum brazing is also used for air conditioning components, pipes, heat exchangers, etc.;
- Aluminum brazing is also used in aerospace components, medical devices, and other critical and non-critical applications.Quick Quote

Non-clad Brazing Aluminum Strip for Vehicles

Brazed Composite Aluminum Sheet

Automotive Brazing Clad Aluminum Coil

Aerospace Aluminum Welding Wire Rod

4043 4047 Aluminium Wire for Welding

Aluminum Alloy Welding Wires
The difference among fusion welding, pressure welding and brazing
Fusion welding
Fusion welding is to use an external heat source (such as an electric arc) to locally heat and melt the area near the interface of the connected components (ie base metal), and then cool to form a joint.
During the welding process, both the base metal and the filler metal are melted, and the two are chemically combined. Such as: manual arc welding, CO2 welding, TIG welding, MIG welding, submerged arc welding, MAG welding, plasma welding, laser welding, electron beam welding, etc.
Pressure welding
Pressure welding is to apply pressure to make the atomic distance of the welded surface close to the lattice distance.
Solder is not used during welding, the metals to be connected are chemically or physically combined, the weld seam is narrow, and the heat-affected area is small, including resistance welding (spot welding, seam welding), flash welding, friction welding, cold pressure welding, etc.
Brazing
Brazing is to realize the connection of the parts to be brazed by melting the metal (brazing filler metal). The temperature of the brazing filler metal is lower than that of the base metal. When welding, the solder melts and the base metal does not melt, and there is a physical combination between the two.
It is customary to divide it into hard brazing and soft brazing with a welding temperature of 450°C. Brazing mainly includes flame brazing, induction brazing, furnace brazing, resistance brazing, etc.