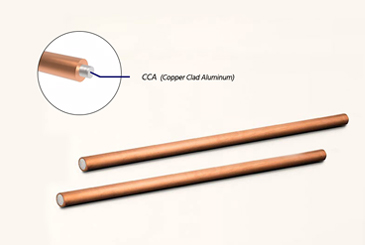
As industrial technology advances, copper-clad aluminum products are becoming more widely used in power, electronics, and construction industries, becoming a key market choice. Combining copper's excellent conductivity with aluminum's lightweight properties, they meet high performance standards while reducing costs. With improved manufacturing processes, the range and specifications of copper-clad aluminum products continue to grow, making them an ideal choice for various industries.
Currently, the common types of copper-clad aluminum products in the market include the following, which are also our key offerings:
In this article, we will explore the key differences between copper and aluminum, as well as the unique advantages of copper-clad aluminum, to help you make a more informed decision when selecting the right product.
8 Key Differences Between Copper and Aluminum
1. Conductivity and Resistance of copper and aluminum
Copper cladded aluminum (CCA) combines the high conductivity of copper with the lightweight properties of aluminum. While copper offers superior conductivity (100% IACS), CCA's conductivity is lower than pure copper but still efficient for many applications, making it a cost-effective alternative for lower-performance uses.
Winner: Copper √
2. Different Ampacity of copper and aluminum
Due to its higher conductivity, copper has a greater ampacity, allowing it to carry more current without overheating compared to CCA. CCA busbars can still handle significant current loads but may need larger sizes to match copper’s current carrying capacity in high-demand applications.
Winner: Copper √
3. Corrosion Resistance of copper and aluminum
Copper exhibits excellent corrosion resistance due to its natural protective verdigris layer. CCA, while offering some corrosion resistance, may require extra protection in highly corrosive environments, particularly where the aluminum core is exposed. Pure copper is better suited for long-term resistance to oxidation and wear.
Winner: Copper √
4. Strength and Durability of copper and aluminum
Copper is more rigid and stronger compared to CCA, which benefits from the lightweight properties of aluminum but sacrifices some mechanical strength. CCA’s aluminum core can also be more susceptible to mechanical stresses and deformations under extreme conditions, whereas copper maintains structural integrity under demanding loads.
Winner: Copper √
5. Thermal Expansion of copper and aluminum
Aluminum, as the core material of CCA, has a higher thermal expansion coefficient than copper. This can lead to instability in connections over temperature fluctuations, especially for CCA products. Copper’s lower expansion rate ensures more stable connections and a longer lifespan in varying temperature conditions.
Winner: Copper √
6. Weight difference of copper and aluminum
CCA benefits from aluminum’s lightweight characteristics, making it an ideal choice for weight-sensitive applications, such as aerospace or transportation. Copper, while heavier, provides superior performance but requires more effort for handling, installation, and transportation.
Winner: CCA √
7. Cost Comparison of copper and aluminum
Copper is more expensive due to its higher conductivity and manufacturing complexity. CCA, on the other hand, provides a lower-cost alternative by using aluminum as the core, offering a cost-effective solution without significantly sacrificing performance in many applications.
Winner: CCA √
8. Environmental Sustainability of copper and aluminum
Both copper and aluminum are recyclable, but CCA’s use of aluminum increases its sustainability, as aluminum has a higher recovery rate and requires significantly less energy to recycle compared to copper. This makes CCA a more environmentally friendly option in many cases.
Winner: CCA √
Explore Chalco's copper-clad aluminum products
Combines copper's high conductivity with aluminum's lightweight, ideal for power transmission, communications, and cables.
Contact us now

Offers copper conductivity with aluminum's lightness, used in high-current applications like power distribution and substations.
Contact us nowCopper-clad Aluminum Sheet
Merges copper's conductivity with aluminum's lightness, commonly used in automotive, power, and construction industries.
Contact us now

Copper-clad Aluminum Tube
Used in heat exchangers and power distribution, providing high conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Contact us nowCopper-clad Aluminum Coil Strip
Ideal for electrical conductors and connectors, combining copper conductivity with aluminum's lightweight properties.
Contact us now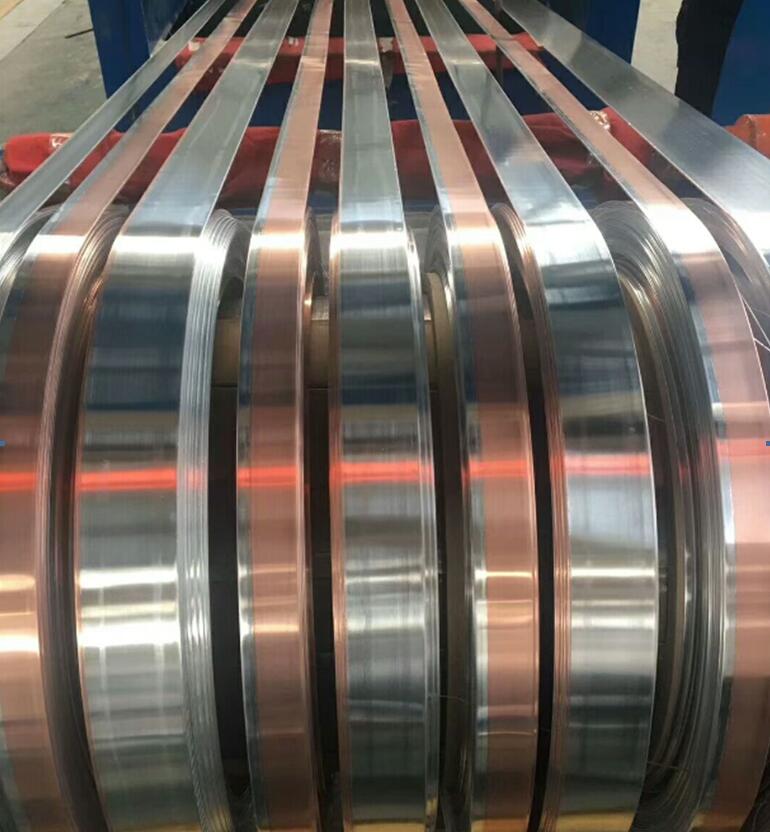
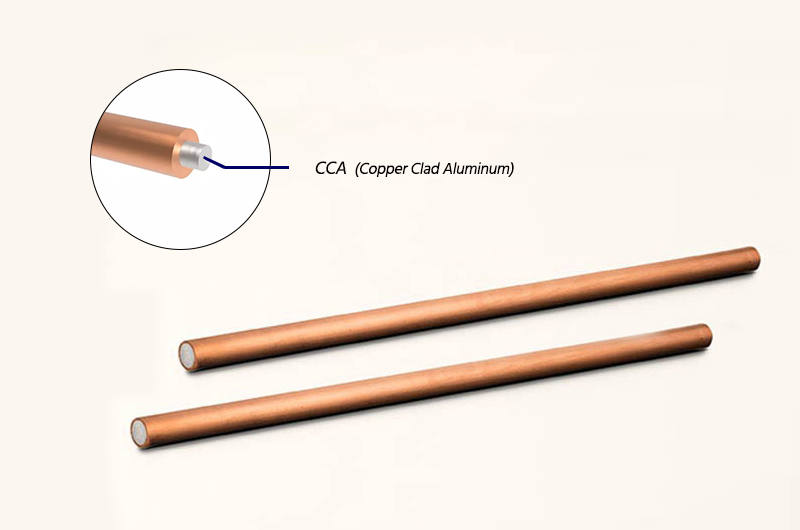
Copper-clad Aluminum Rod
Used in electrical connectors and busbars, offering high durability and conductivity with reduced weight.
Contact us nowCopper Clad Aluminum industry application and projct solutions
Copper clad aluminum (CCA) materials offer an optimal balance of conductivity, weight, and cost, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial applications. From electrical power transmission to transportation and telecommunications, Chalco's CCA products provide tailored solutions that enhance performance and efficiency. Our expertise enables us to support diverse projects with high-quality materials engineered to meet stringent industry standards and specific operational demands.
Instant QuoteChalco's integrated solution for power industry — copper or aluminum or CCA?
Considering the advantages of copper-aluminum products, copper-aluminum composites have become a key solution in the power industry. Combining copper's conductivity with aluminum's light weight, strength, and corrosion resistance, these products offer cost-effective, sustainable, and versatile solutions.
Contact us now
| When to Use Copper Busbars | When to Use Aluminum Busbars | When to Use Copper-Clad Aluminum Busbars |
| High-Performance Systems: Ideal for power generation, transmission, and high-power electronics due to high conductivity. Critical Infrastructure: Suited for projects where reliability and longevity are crucial, like substations and data centers. Harsh Environments: Preferred in outdoor or corrosive environments for its high corrosion resistance. Low-Resistance Connections: Best for high-current applications, motor control centers, and distribution panels. | Cost-Sensitive Applications: Chosen for projects where cost is a key factor. Lightweight Applications: Ideal in aerospace, automotive, and portable electronics due to its lighter weight. Heat Dissipation: Better at dissipating heat, preventing overheating in thermal-sensitive applications. Flexible Applications: Easier to bend and manufacture, making it suitable for busway systems. Utility-Scale Power: Standard in large-scale power systems due to lower cost and suitability for high-voltage transmission. | Balanced Performance and Cost: Offers better conductivity than aluminum and is more cost-effective than copper. Moderate Corrosive Environments: Suitable for environments needing decent corrosion resistance. Weight-Conscious with High Conductivity: Ideal when weight savings are important, but higher conductivity is needed. |
Copper-Clad Aluminum Bus Bar
a third-gen conductor in power systemst……

Copper-clad aluminum CCA wire
Combining copper's conductivity, aluminum's lightweight……
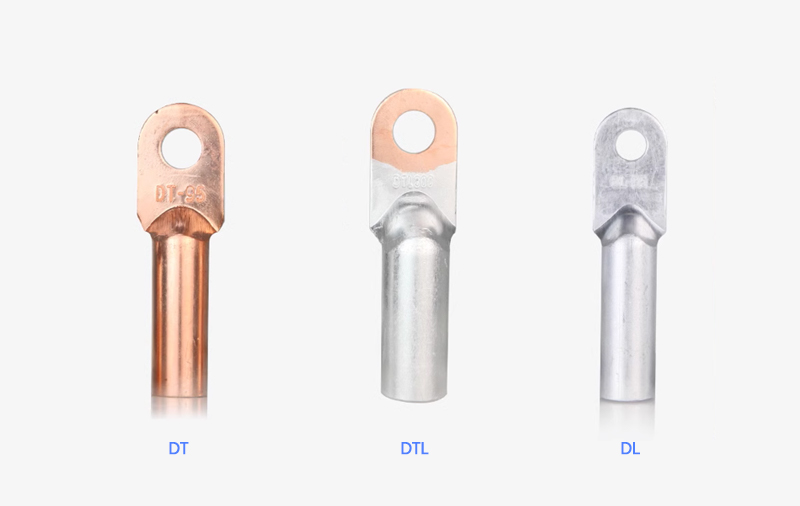

Copper-aluminum Connecting Terminals
Widely used in distribution, transformers, and cable……
CCA bus or bimetallic conductive bus, it is the third generation of "new energy-saving conductor materials".
Conductivity Scalability Reliability- 6101 EC aluminum busbar T6, T61, T63, T64, T65
Containing magnesium and silicon, has high mechanical strength. Better anti creep than 1350.
Thermal stability Easy processing - 1060 EC aluminum busbar T3, T4, T5, T6, T8
It is usually formed by extrusion or rolling, and has good processing performance.
High conductivity Corrosion resistance - 1350 EC aluminum busbar H14, H16, H19
The minimum weight percentage is 99.5%, which is the material used for battery busbars.
Conductivity Thermal conductivity - 6060 EC aluminum busbar T4, T5, T6
It can effectively transmit and distribute electricity, reducing energy loss and line power loss.
Lightweight Processability - 6082 EC aluminum busbar T3, T4, T5, T6
It has high strength and hardness, while maintaining good conductivity.
Machinability High strength and rigidity 6061 aluminum busbar has strong conductivity and is a universal material for most processing technologies.
Smooth surface Strong moisture resistance- 6063 EC aluminum busbar T4, T5, T6, T52, T66
In high-power applications, it can help effectively dissipate heat, and reduce the risk of equipment overheating.
Strong plasticity Excellent heat dissipation
Chalco's CCA products for Electronics Industry
Copper-aluminum composites are ideal for electronic components, connectors, and cooling systems, thanks to their high conductivity, corrosion resistance, and light weight. They help improve device performance and durability while minimizing weight.
Contact us now
Chalco's CCA products for Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, especially for electric vehicles, copper-aluminum composites reduce weight and improve power system efficiency, making them essential for battery management and power transmission in electric vehicles.
Contact us now
Chalco's CCA products for Heat Exchange Systems
Copper-aluminum composites are ideal for heat exchange systems, with copper providing excellent thermal conductivity and aluminum offering strength and reduced weight. These materials are widely used in air conditioners, heat exchangers, and cooling systems.
Contact us now
Chalco composite copper-aluminum bonding technologies — Our Processing Advantage
Chalco Composite leads the industry in advanced copper-aluminum bonding technologies, delivering superior composite materials that combine the best properties of both metals. Our state-of-the-art processing methods ensure exceptional bonding strength, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance, tailored to meet the demanding requirements of electrical, transportation, and industrial applications. Whether through explosive welding, hot rolling cladding, or precision co-extrusion, Chalco Composite guarantees reliable performance and consistent quality in every product.
Instant QuoteExplosive Welding
Explosive welding is a solid-state bonding method that joins dissimilar metals like copper and aluminum using high-velocity impact. Chalco Composite excels in large-format explosive cladding with controlled interfacial waveforms, ensuring excellent bonding strength and conductivity for critical electrical applications.
Hot Rolling Cladding
This method bonds copper and aluminum under high temperature and pressure to produce large-area composite coils and plates. Chalco Composite leverages advanced hot rolling lines to ensure smooth surfaces, accurate thickness ratios, and excellent formability— ideal for structural and electrical stamping parts.
Co-extrusion & Drawing
In this process, a copper layer is concentrically extruded over an aluminum core, then drawn through precision dies to achieve high-quality bonding and tight dimensional tolerances. Chalco Composite ensures consistent copper coverage and excellent electrical performance for round and shaped conductive components.
Advantages of Chalco Copper clad aluminum CCA products
- Excellent Conductivity:The copper outer layer of CCA materials provides excellent conductivity, ensuring high electrical transmission efficiency, making it suitable for applications requiring high conductivity.
- Lightweight:Aluminum has a density that is only one-third of copper, making CCA materials much lighter than pure copper. This significantly reduces the weight of cables and wires, facilitating easier transportation and installation, especially in industries like aviation and automotive where weight reduction is critical.
- Cost-Effective:Aluminum is less expensive than copper, so the manufacturing cost of CCA materials is lower than that of pure copper. This makes it more economical for large-scale applications without significantly compromising performance.
- Good Mechanical Properties:CCA materials possess good strength and toughness, capable of withstanding considerable mechanical stress and tension, making them suitable for various demanding environments.
- Corrosion Resistance:The copper outer layer provides excellent corrosion resistance, protecting the aluminum core from oxidation and corrosion, thereby enhancing the material's durability and lifespan.
- Flexibility and Ease of Processing:CCA materials combine the solderability of copper with the flexibility of aluminum, making them easier to handle during manufacturing and processing. This makes them ideal for complex electrical designs and installations.
Through these advantages, copper-clad aluminum conductive materials have found widespread use in cables, wires, electronic components, and more, providing an economical, efficient, and high-performance conductive solution.
Instant QuoteComprehensive Guide to Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA) Products——Knowledge and Technical Specifications
How to convert copper busbar sizes to aluminum for electrical projects while maintaining the same temperature rise
In electrical applications, the choice between copper and aluminum busbars often requires consideration of temperature rise differences. To substitute aluminum busbars for copper while maintaining the same temperature rise, adjustments to the aluminum busbar size must be made to account for its different conductivity. There are two common methods for making this conversion.
- First Method: Increase the Width of the Aluminum Bar: By increasing the width of the aluminum bar by approximately 27%, the same temperature rise effect as a copper bar can be achieved. For example, a 5-inch x 1/4-inch aluminum bar is equivalent to a 4-inch x 1/4-inch copper bar. This method effectively increases the cross-sectional area, reducing resistive heating and enhancing heat dissipation.
- Second Method: Increase the Thickness of the Aluminum Bar: Another approach is to increase the thickness of the aluminum bar by approximately 50%. For example, a 4-inch x 3/8-inch aluminum bar can match the temperature rise effect of a 4-inch x 1/4-inch copper bar. While this method also increases the cross-sectional area, changes in thickness have a smaller impact on heat dissipation, making it less effective than increasing the width.
In both conversion methods, the thermal skin effect must also be considered. This effect occurs under high current conditions, where the internal temperature of the conductor rises faster than the external temperature because the outer parts dissipate heat more efficiently. This leads to higher internal resistance and greater voltage drop, generating more heat. Therefore, when designing aluminum busbars, it is important to consider both size adjustments and the thermal skin effect to ensure system safety and stability.
Reference Table of Specifications
| Converting Copper to Aluminum using an Ampacity Chart | ||||||||||||
| Ampacity Conversion Chart | Copper C110 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | Aluminum 6101 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | ||||
| Flat Bar Size in Inches | Sq. In | Circ Mils Thousands | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp* | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp** | ||||
| 1/2*1 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.93 | 16.5 | 620 | 820 | 940 | 0.585 | 31 | 347 | 459 | 526 |
| 1/2*1 1/2 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.9 | 11 | 830 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.878 | 21 | 465 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/2*2 | 1 | 1270 | 3.86 | 8.23 | 1000 | 1350 | 1550 | 1.17 | 15 | 560 | 756 | 868 |
| 1/2*2 1/2 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.83 | 6.58 | 1200 | 1600 | 1850 | 1.463 | 12 | 672 | 896 | 1036 |
| 1/2*3 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.8 | 5.49 | 1400 | 1850 | 2150 | 1.755 | 10 | 784 | 1036 | 1204 |
| 1/2*3 1/2 | 1.75 | 2230 | 6.76 | 4.7 | 1550 | 2100 | 2400 | 2.048 | 9 | 868 | 1176 | 1344 |
| 1/2*4 | 2 | 2550 | 7.73 | 4.11 | 1700 | 2300 | 2650 | 2.34 | 8 | 952 | 1288 | 1484 |
| 1/2*5 | 2.5 | 3180 | 9.66 | 3.29 | 2050 | 2750 | 3150 | 2.925 | 6 | 1148 | 1540 | 1764 |
| 1/2*6 | 3 | 3820 | 11.6 | 2.74 | 2400 | 3150 | 3650 | 3.51 | 5 | 1344 | 1764 | 2044 |
| 1/2*8 | 4 | 5090 | 15.5 | 2.06 | 3000 | 4000 | 4600 | 4.68 | 4 | 1680 | 2240 | 2576 |
| 1/4*1/2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 240 | 315 | 360 | 0.146 | 123 | 134 | 176 | 202 |
| 1/4*3/4 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 320 | 425 | 490 | 0.220 | 82 | 179 | 238 | 274 |
| 1/4*1 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 400 | 530 | 620 | 0.293 | 62 | 224 | 297 | 347 |
| 1/4*1 1/2 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 560 | 740 | 880 | 0.439 | 41 | 314 | 414 | 482 |
| 1/4*2 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.585 | 31 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/4*2 1/2 | 0.625 | 796 | 2.410 | 13.2 | 850 | 1150 | 1300 | 0.731 | 25 | 476 | 644 | 728 |
| 1/4*3 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.900 | 11 | 990 | 1300 | 1550 | 0.878 | 21 | 554 | 728 | 868 |
| 1/4*3 1/2 | 0.875 | 1110 | 3.380 | 9.4 | 1150 | 1500 | 1750 | 1.024 | 18 | 644 | 840 | 980 |
| 1/4*4 | 1 | 1270 | 3.860 | 8.23 | 1250 | 1700 | 1950 | 1.170 | 15 | 700 | 952 | 1092 |
| 1/4*5 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.830 | 6.58 | 1500 | 2000 | 2350 | 1.463 | 12 | 840 | 1120 | 1316 |
| 1/4*6 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.800 | 5.49 | 1750 | 2350 | 2700 | 1.755 | 10 | 980 | 1316 | 1512 |
| 1/8*1/2 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.241 | 132 | 153 | 205 | 235 | 0.073 | 247 | 86 | 115 | 132 |
| 1/8*3/4 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 215 | 285 | 325 | 0.110 | 164 | 120 | 160 | 182 |
| 1/8*1 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 270 | 360 | 415 | 0.146 | 123 | 151 | 202 | 232 |
| 1/8*1 1/2 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 385 | 510 | 590 | 0.220 | 82 | 216 | 286 | 330 |
| 1/8*2 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 495 | 660 | 760 | 0.293 | 62 | 277 | 370 | 426 |
| 1/8*2 1/2 | 0.312 | 397 | 1.210 | 26.4 | 600 | 800 | 920 | 0.365 | 49 | 336 | 448 | 515 |
| 1/8*3 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.439 | 41 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/8*3 1/2 | 0.438 | 558 | 1.690 | 18.8 | 810 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.512 | 35 | 454 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/8*4 | 0.5 | 636 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 900 | 1200 | 1400 | 0.585 | 31 | 504 | 672 | 784 |
| 1/16*1/2 | 0.0312 | 39.7 | 0.121 | 264 | 103 | 136 | 157 | 0.037 | 494 | 58 | 76 | 88 |
| 1/16*3/4 | 0.0469 | 59.7 | 0.181 | 175 | 145 | 193 | 225 | 0.055 | 327 | 81 | 108 | 126 |
| 1/16*1 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.242 | 132 | 187 | 250 | 285 | 0.073 | 247 | 105 | 140 | 160 |
| 1/16*1 1/2 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 270 | 355 | 410 | 0.110 | 164 | 151 | 199 | 230 |
| 1/16*2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 345 | 460 | 530 | 0.146 | 123 | 193 | 258 | 297 |
| Source: Copper Development Organization; Aluminum Association | ||||||||||||
| Note: Ratings depend upon configuration, air flow, ambient temp, etc. The values depicted are an approximation. Controlled testing is always required to validate. | ||||||||||||
| Other considerations Forming the busbar (aluminum has a tendency to crack with very tight radius) Electroplating the busbar (white rust on aluminum, oxidation is an issue with aluminum) Configuration of the busbar (vertical or horizontal configuration) | ||||||||||||
| Copper | AL 6101 | AL 1350 | AL 6061 | AL 6063 | AL 1050 | AL 1060 | AL 1070 | |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS) | 100% | 50% - 55% | 61% - 62% | 40% - 43% | 52% - 56% | 61% | 61% | 62% |
| Specific resistance (ohmscir/mil ft) (20℃ ref) | 10.6 | 18.52 | ||||||
Chalco can provide you the most comprehensive inventory of aluminum products and can also supply you customized products. Precise quotation will be provided within 24 hours.
Get a quote