Busbars are typically made of conductive metals such as copper or aluminum. These materials are chosen due to their excellent electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and relatively low cost. Copper is often preferred for its superior conductivity and thermal performance, while aluminum is favored in applications where weight and cost are significant considerations. In some cases, busbars may also be coated or plated with materials like tin or silver to enhance their conductivity and resistance to oxidation.
Chalco-reliable supplier of conductive aluminum busbar products
- Chalco's electrical busbar products are comprehensive, covering aluminum busbars, copper busbars, copper clad aluminum busbars. Hot selling aluminum busbar products include 6101, 1050, 1060, 1070, 1100, 1350, 6061, 6063, 6082... Widely used in electrical conductors of distribution systems.
- Chalco EC grade aluminum busbar, complying with standards such as ASTM B317, ASTM B236, IEC 60105, ISO 209-1, 2, DIN EN 755-2, EN 573-3, etc., is widely used in electrical conductors of distribution systems.
- Chalco specializes in providing various conductive aluminum busbar products and has established connections with a large number of manufacturers in transformers, switchgear, power capacitors, power tools, etc. fields.

Chalco conductive aluminum busbar
-
6101 EC aluminum busbar T6, T61, T63, T64, T65
Containing magnesium and silicon, has high mechanical strength. Better anti creep than 1350.
Thermal stability Easy processing -
1060 EC aluminum busbar T3, T4, T5, T6, T8
It is usually formed by extrusion or rolling, and has good processing performance.
High conductivity Corrosion resistance -
1350 EC aluminum busbar H14, H16, H19
The minimum weight percentage is 99.5%, which is the material used for battery busbars.
Conductivity Thermal conductivity -
6060 EC aluminum busbar T4, T5, T6
It can effectively transmit and distribute electricity, reducing energy loss and line power loss.
Lightweight Processability -
6082 EC aluminum busbar T3, T4, T5, T6
It has high strength and hardness, while maintaining good conductivity.
Machinability High strength and rigidity -
6061 aluminum busbar has strong conductivity and is a universal material for most processing technologies.
Smooth surface Strong moisture resistance -
6063 EC aluminum busbar T4, T5, T6, T52, T66
In high-power applications, it can help effectively dissipate heat, and reduce the risk of equipment overheating.
Strong plasticity Excellent heat dissipation -
For more alloy products or customized requirements, please contact us.
Chalco conductive copper busbar
Chalco uses advanced CNC technology in copper busbar manufacturing to deliver efficient production and solutions. Our in-house CNC capabilities save time and costs, using presses, bending machines, lasers, and more. We meet standards like AS9100D and ISO9001:2015 and offer quick prototyping for customer evaluation.
Contact us now
- Reduce System Costs: Chalco copper busbars help lower overall system expenses through efficient design and manufacturing.
- Improve Reliability and Thermal Performance: Enhanced reliability and heat management ensure long-lasting and stable performance.
- Eliminate Wiring Errors: Pre-assembled busbars eliminate the complexity of wiring, reducing installation errors.
- Lower Inductance and Impedance: The design minimizes inductance and impedance, enhancing electrical efficiency.
- Provide More Interconnection Options: Multiple interconnection choices make it adaptable for various electrical systems.
- Save Time and Costs: Our in-house coating process streamlines production, reducing the need for outsourcing and cutting costs.
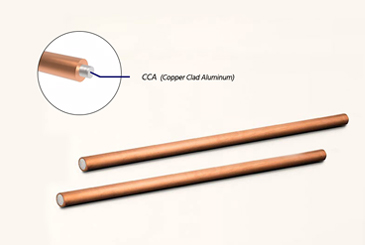
Chalco copper clad aluminum busbar and laminated busbar
Copper clad aluminum busbar: CCA bus or bimetallic conductive bus, it is the third generation of "new energy-saving conductor materials".
Laminated busbar: Laminated busbars consist of multiple conductive metal layers (copper or aluminum) separated by thin dielectric materials, offering advantages like enhanced reliability, reduced heat, and low inductance compared to single-layer busbars and cables.
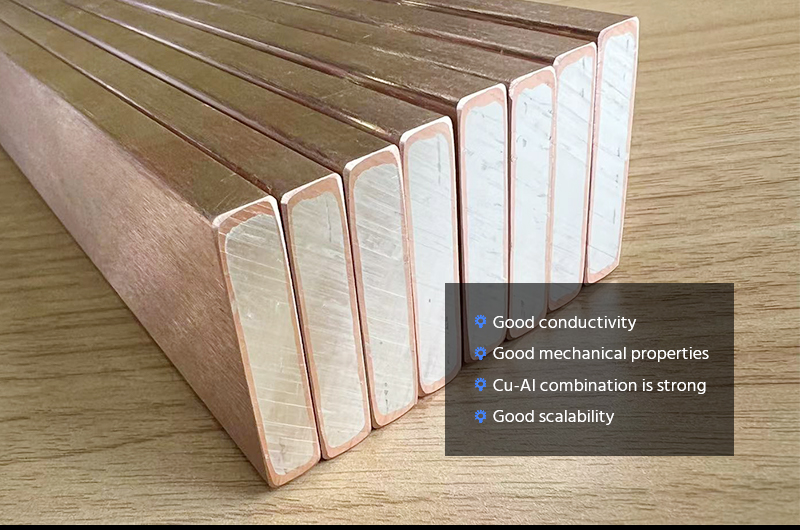

Advantages of Copper-Clad Aluminum Busbars
- Lighter Weight: Reduces transportation and installation costs.
- Excellent Conductivity: Copper layer provides high electrical conductivity.
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum core with copper cladding offers a budget-friendly solution.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper coating protects against corrosion, extending lifespan.
- Mechanical Strength: Strong and flexible, ideal for complex electrical installations.
Advantages of Laminated Busbars
- Reliability: Compact pre-assembly reduces installation errors and ensures performance with HiPot and partial discharge testing.
- Heat Reduction: Compact design and cooling plates lower heat and improve airflow efficiency.
- Low Inductance: Multi-layer structure minimizes stray inductance, enhancing system efficiency.
- Clean Energy Applications: Paired with IGBT, supports efficient power in solar and wind sectors.
- Edge Sealing: Options include open edge, crimped seal, and epoxy filling.
Manufacturing Processing and Customization capabilities
Chalco Aluminum is a leading manufacturer of high-performance aluminum busbars, offering comprehensive processing, customization, and manufacturing capabilities to meet diverse industrial and electrical applications. Our state-of-the-art facilities ensure precision machining, advanced material cladding, and high-quality surface treatments to enhance performance, durability, and reliability.
Surface treatment for enhanced performance
To improve the durability, conductivity, and corrosion resistance of our aluminum busbars, we offer the following surface treatments:
- Anodizing – Forms a dense oxide layer for enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Electroplating – Silver, tin, or nickel plating to increase electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance.
- Protective Spraying – Ensures long-term performance in harsh environments.
Customization & quality assurance
We support custom orders based on specific electrical and mechanical requirements, including:
- Custom dimensions – Thickness 0.15mm - 40mm, Width 10mm - 200mm, Length up to 6m.
- Special bending and forming – Tailored to fit unique electrical layouts.
- Stringent testing procedures – Including conductivity tests, temperature rise tests, and bending tests to guarantee optimal performance.
Precision machining & fabrication
We provide advanced machining services to achieve precise dimensions and structural integrity for various applications:
- Cutting – Custom length adjustments for different installations.
- Drilling – Precision hole placement for electrical connections.
- Bending – Tailored shaping to fit complex assembly requirements.
- Stamping – High-efficiency mass production for uniform busbar components.
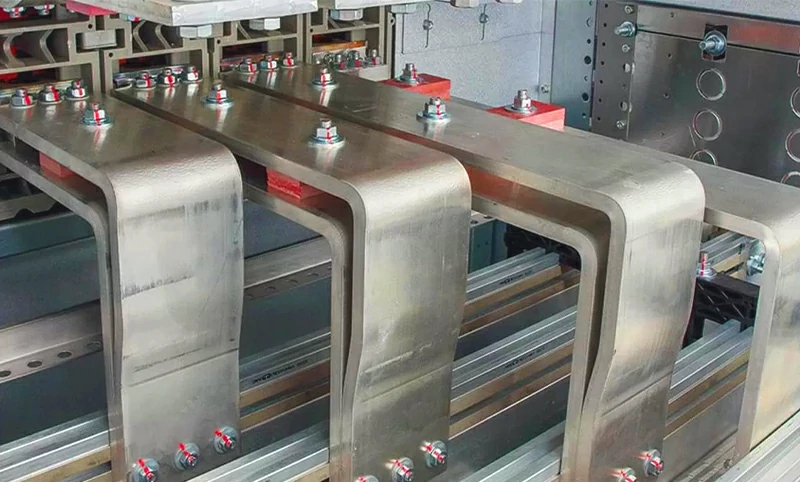


Copper cladding & insulation coating
Our specialized cladding and insulation techniques enhance conductivity, corrosion resistance, and electrical safety:
- Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA) Processing – Utilizing explosive welding, rolling cladding, and hot-dip cladding to form a high-strength copper-aluminum composite layer, improving conductivity and mechanical performance.
- Insulation Coatings – Powder coating, epoxy resin coating to prevent electrical leakage and corrosion.
- Insulation Sleeves – Options include PVC, heat shrink tubing, and silicone rubber, ensuring additional protection in high-voltage applications.


At Chalco Aluminum, we combine high-precision manufacturing with advanced processing technologies, ensuring reliable, high-quality aluminum and copper-clad busbars for global industrial and electrical applications.
For further inquiries or customized solutions, contact us today for a quick quote!Quick Quote
Chalco offers more than just busbar products—Comprehensive Solutions for Your Projects
At Chalco, we deliver not only top-quality copper and aluminum busbars but also complete project solutions tailored to your needs. Our aluminum busbars and electrical connectors are ideal for power distribution systems, offering cost-effective, reliable performance.
1. Temperature Rise Management
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has lower thermal conductivity than copper, requiring an increase in surface area to enhance heat dissipation efficiency. Copper's superior thermal conductivity allows for higher heat dissipation efficiency, but good ventilation design is still necessary to optimize performance.
- Heat Exchange: The design should consider better heat exchange mechanisms to compensate for aluminum's thermal conductivity shortcomings.
2. Available Space Size Design
- Aluminum is ightweight and easy to handle, suitable for compact spaces. Copper, typically heavier, requires careful consideration of its impact on supporting structures.
- Custom Design: Ensure that busbars fit the space limitations of cabinets, switchgear, and distribution panels.
3. Installation Methods and Locations
- Industry Standards: Follow IEEE, UL, and NEMA standards to determine the feasibility of using connectors and bus systems.
- Experience and Knowledge: Design engineers should recommend the best installation locations and methods based on material properties.
4. Maintenance Management
- Corrosion and Thermal Expansion/Contraction: Aluminum, regularly check for corrosion and monitor thermal expansion/contraction. Copper has better corrosion resistance, but regular inspections are still necessary in harsh environments.
- Fastener Management: It is strongly recommended to regularly inspect fasteners and establish a torque plan to prevent loosening.
5. Protection Options
- Coating Protection: Consider dielectric coatings, such as epoxy powder coatings, to enhance environmental protection.
- Diverse Design: Both aluminum and copper allow for the use of laminated busbars and insulated bus connectors, increasing design flexibility.
6. Mechanical Fastening Risks
- Loosening Risk: Aluminum has higher thermal expansion (42% more than copper) increases the risk of loosening fasteners. Copper has lower thermal expansion, but contact resistance can still change over time.
- Deformation Prevention Measures: Provide torque sequence information and specifications for connection washers and bolts to help prevent deformation of connections.
When installing copper and aluminum busbars, attention to performance, safety, and durability is essential. Although there are similarities, the different material properties require that copper busbars focus more on weight and thermal management, while corrosion protection measures must also be carefully considered.
Copper vs aluminum-choose the correct material for your project
There is debate over whether aluminum or copper is more suitable for busbars, as both have been successfully used. In the past 50 years, busbars have evolved beyond traditional distribution, with recent innovations shifting demand from copper to aluminum. Despite some misconceptions about aluminum, both materials can meet requirements if manufactured and installed correctly.
There is debate over whether aluminum or copper is more suitable for busbars, as both have been successfully used. In the past 50 years, busbars have evolved beyond traditional distribution, with recent innovations shifting demand from copper to aluminum. Despite some misconceptions about aluminum, both materials can meet requirements if manufactured and installed correctly.
If you have an electrical project and want to find the most suitable material for it, please feel free to contact Chalco. We will address all your questions regarding copper and aluminum busbars.Quick Quote

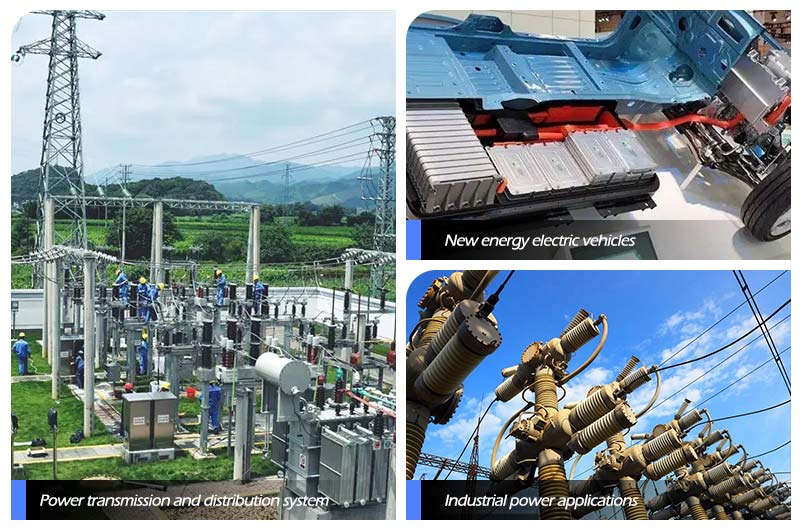
Service field and cooperative partner of Chalco electrical busbar
Power transmission and distribution system: can be used in high-voltage transmission lines, substations, distribution transformers, and other power equipment.
Industrial power applications: such as factories, mines, and manufacturing facilities.
Buildings and building facilities: can be located in the distribution room and power box inside the building.
New energy systems: such as solar and wind power generation systems. They are used to convert new energy into electrical energy and transmit it to the power grid or energy storage equipment.
New energy electric vehicles: with the popularization of new energy electric vehicles, conductive aluminum busbars are also widely used in electric vehicle drive systems and charging stations. The high conductivity and lightweight performance of aluminum can not only meet the requirements of reaching the point, but also meet the requirements of automotive lightweight.

Ampacity chart of copper and aluminum busbar
| Converting Copper to Aluminum using an Ampacity Chart | ||||||||||||
| Ampacity Conversion Chart | Copper C110 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | Aluminum 6101 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | ||||
| Flat Bar Size in Inches | Sq. In | Circ Mils Thousands | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp* | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp** | ||||
| 1/2*1 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.93 | 16.5 | 620 | 820 | 940 | 0.585 | 31 | 347 | 459 | 526 |
| 1/2*1 1/2 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.9 | 11 | 830 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.878 | 21 | 465 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/2*2 | 1 | 1270 | 3.86 | 8.23 | 1000 | 1350 | 1550 | 1.17 | 15 | 560 | 756 | 868 |
| 1/2*2 1/2 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.83 | 6.58 | 1200 | 1600 | 1850 | 1.463 | 12 | 672 | 896 | 1036 |
| 1/2*3 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.8 | 5.49 | 1400 | 1850 | 2150 | 1.755 | 10 | 784 | 1036 | 1204 |
| 1/2*3 1/2 | 1.75 | 2230 | 6.76 | 4.7 | 1550 | 2100 | 2400 | 2.048 | 9 | 868 | 1176 | 1344 |
| 1/2*4 | 2 | 2550 | 7.73 | 4.11 | 1700 | 2300 | 2650 | 2.34 | 8 | 952 | 1288 | 1484 |
| 1/2*5 | 2.5 | 3180 | 9.66 | 3.29 | 2050 | 2750 | 3150 | 2.925 | 6 | 1148 | 1540 | 1764 |
| 1/2*6 | 3 | 3820 | 11.6 | 2.74 | 2400 | 3150 | 3650 | 3.51 | 5 | 1344 | 1764 | 2044 |
| 1/2*8 | 4 | 5090 | 15.5 | 2.06 | 3000 | 4000 | 4600 | 4.68 | 4 | 1680 | 2240 | 2576 |
| 1/4*1/2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 240 | 315 | 360 | 0.146 | 123 | 134 | 176 | 202 |
| 1/4*3/4 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 320 | 425 | 490 | 0.220 | 82 | 179 | 238 | 274 |
| 1/4*1 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 400 | 530 | 620 | 0.293 | 62 | 224 | 297 | 347 |
| 1/4*1 1/2 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 560 | 740 | 880 | 0.439 | 41 | 314 | 414 | 482 |
| 1/4*2 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.585 | 31 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/4*2 1/2 | 0.625 | 796 | 2.410 | 13.2 | 850 | 1150 | 1300 | 0.731 | 25 | 476 | 644 | 728 |
| 1/4*3 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.900 | 11 | 990 | 1300 | 1550 | 0.878 | 21 | 554 | 728 | 868 |
| 1/4*3 1/2 | 0.875 | 1110 | 3.380 | 9.4 | 1150 | 1500 | 1750 | 1.024 | 18 | 644 | 840 | 980 |
| 1/4*4 | 1 | 1270 | 3.860 | 8.23 | 1250 | 1700 | 1950 | 1.170 | 15 | 700 | 952 | 1092 |
| 1/4*5 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.830 | 6.58 | 1500 | 2000 | 2350 | 1.463 | 12 | 840 | 1120 | 1316 |
| 1/4*6 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.800 | 5.49 | 1750 | 2350 | 2700 | 1.755 | 10 | 980 | 1316 | 1512 |
| 1/8*1/2 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.241 | 132 | 153 | 205 | 235 | 0.073 | 247 | 86 | 115 | 132 |
| 1/8*3/4 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 215 | 285 | 325 | 0.110 | 164 | 120 | 160 | 182 |
| 1/8*1 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 270 | 360 | 415 | 0.146 | 123 | 151 | 202 | 232 |
| 1/8*1 1/2 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 385 | 510 | 590 | 0.220 | 82 | 216 | 286 | 330 |
| 1/8*2 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 495 | 660 | 760 | 0.293 | 62 | 277 | 370 | 426 |
| 1/8*2 1/2 | 0.312 | 397 | 1.210 | 26.4 | 600 | 800 | 920 | 0.365 | 49 | 336 | 448 | 515 |
| 1/8*3 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.439 | 41 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/8*3 1/2 | 0.438 | 558 | 1.690 | 18.8 | 810 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.512 | 35 | 454 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/8*4 | 0.5 | 636 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 900 | 1200 | 1400 | 0.585 | 31 | 504 | 672 | 784 |
| 1/16*1/2 | 0.0312 | 39.7 | 0.121 | 264 | 103 | 136 | 157 | 0.037 | 494 | 58 | 76 | 88 |
| 1/16*3/4 | 0.0469 | 59.7 | 0.181 | 175 | 145 | 193 | 225 | 0.055 | 327 | 81 | 108 | 126 |
| 1/16*1 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.242 | 132 | 187 | 250 | 285 | 0.073 | 247 | 105 | 140 | 160 |
| 1/16*1 1/2 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 270 | 355 | 410 | 0.110 | 164 | 151 | 199 | 230 |
| 1/16*2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 345 | 460 | 530 | 0.146 | 123 | 193 | 258 | 297 |
| Source: Copper Development Organization; Aluminum Association | ||||||||||||
| Note: Ratings depend upon configuration, air flow, ambient temp, etc. The values depicted are an approximation. Controlled testing is always required to validate. | ||||||||||||
| Other considerations Forming the busbar (aluminum has a tendency to crack with very tight radius) Electroplating the busbar (white rust on aluminum, oxidation is an issue with aluminum) Configuration of the busbar (vertical or horizontal configuration) | ||||||||||||
Conductive aluminum busbar size reference table
| Square angle aluminum bar | ||||||||||
| 2mm | 2*30 | 2*40 | 2*67 | 2*70 | 2.5* 25 | |||||
| 3mm | 3*10 | 3*15 | 3*20 | 3*25 | 3*30 | 3*40 | 3*50 | 3*60 | 3*67 | 3*75 |
| 3*110 | ||||||||||
| 4mm | 4*10 | 4*15 | 4*20 | 4*25 | 4*30 | 4*40 | 4*45 | 4*50 | 4*60 | 4.6*60 |
| 4.8*9.8 | ||||||||||
| 5mm | 5*15 | 5*20 | 5*25 | 5*30 | 5*35 | 5*40 | 5*50 | 5*60 | 5*80 | 5*100 |
| 6mm | 6*20 | 6*25 | 6*30 | 6*40 | 6*50 | 6*54 | 6*55 | 6*60 | 6*65 | 6*70 |
| 6*75 | 6*80 | 6*100 | 6*120 | 6*150 | 6*160 | |||||
| 6.3mm | 6.3*50 | 6.3*63 | 6.3*63.5 | 6.3*80 | 6.35*50.8 | 6.35*76.2 | ||||
| 7mm | 7.6*80 | 7*150 | 7*4*20*4 | |||||||
| 8mm | 8*11 | 8*30 | 8*40 | 8*50 | 8*51 | 8*60 | 8*63 | 8*63.5 | 8*65 | 8*70 |
| 8*80 | 8*90 | 8*100 | 8*120 | 8*125 | 8.8*28.6 | |||||
| 9mm | 9*170 | 9*125 | 9. 2*64 | |||||||
| 10mm | 10*20 | 10*25 | 10*30 | 10*40 | 10*45 | 10*50 | 10*60 | 10*63 | 10*65 | 10*70 |
| 10*80 | 10*90 | 10*100 | 10*110 | 10*114 | 10*120 | 10*125 | 10*140 | 10*150 | 10*160 | |
| 12mm | 12*30 | 12*40 | 12*45 | 12*50 | 12*60 | 12*70 | 12*76 | 12*80 | 12*100 | 12*120 |
| 12*125 | 12*130 | 12*140 | 12*150 | 12*160 | ||||||
| 12.5mm | 12.5*90 | 12.5*100 | 12.5*125 | 12.5*127 | 12.7*101.6 | 12.7*160 | ||||
| 13mm | 13*125 | 13*130 | 13*160 | |||||||
| 14mm | 14*100 | 14*120 | 14.5*80 | |||||||
| 15mm | 15*30 | 15*35 | 15*50 | 15*60 | 15*80 | 15*100 | 15*120 | 15*125 | 15*150 | |
| 16mm | 16*30 | 16*90 | 16*100 | 16*110 | 16*125 | 16*130 | 16*140 | 16*150 | 16*160 | |
| 20mm | 20*76 | 20*100 | 20*120 | 20*130 | ||||||
| Square bar | 19*19 | 30*45 | 15*15 | |||||||
| Round bar | Φ6 | Φ8 | Φ10 | Φ11 | Φ12 | Φ14 | Φ15 | Φ15.6 | Φ16 | Φ18 |
| Φ20 | Φ21 | Φ22 | Φ23 | Φ25 | Φ27 | Φ28 | Φ30 | Φ32 | Φ35 | |
| Φ38 | Φ40 | Φ45 | Φ50 | Φ55 | Φ60 | |||||
| Round angle aluminum bar | |||||||||
| 2mm | R2*20 | R2.5* 50 | |||||||
| 3mm | R3*30 | R3*40 | R3*50 | R3*60 | R3*80 | R3*100 | R3*120 | R3*160 | |
| 4mm | R4*25 | R4*30 | R4*35 | R4*40 | R4*50 | R4*60 | R4.1*44.1 | R4.7*151 | |
| 5mm | R5*30 | R5*35 | R5*40 | R5*45 | R5*50 | R5*60 | R5*70 | R5*75 | R5*80 |
| R5*90 | R5*100 | R5*120 | |||||||
| 6mm | R6*40 | R6*50 | R6*60 | R6*70 | R6*80 | R6*100 | R6*120 | R6*140 | R6*160 |
| R6.3*63 | R6.35*76.5 | ||||||||
| 7mm | R7*70 | ||||||||
| 8mm | R8*40 | R8*50 | R8*60 | R8*80 | R8*100 | RS*120 | |||
| 10mm | R10*20 | R10*40 | R10*50 | R10*60 | R10*75 | R10*80 | R10*100 | R10*120 | R10*125 |
| R10*150 | R10*160 | R10*170 | R10.4*25 | ||||||
| 12mm | R12*80 | R12*100 | R12*110 | R12*120 | R12*125 | R12*150 | R12*160 | ||
| 12.5mm | R12.5*80 | R12.5*125 | R12.7*90 | R12.7*127 | |||||
| 13mm | R13*120 | R13*125 | |||||||
| 14mm | R14*100 | R14*120 | R14*150 | ||||||
| 15mm | R15*100 | R15*120 | R15*130 | R15*150 | |||||
| 16mm | R16*150 | R16*160 | |||||||
| 19mm | R19.05*101.6 | R19.05*127 | |||||||
| 20mm | R20*80 | R20*120 | R20*130 | ||||||
| Special-shaped hypotenuse | *4*50 | *5*50 | *5*60 | *6*40 | *6*50 | *6*60 | *6*80 | *8*60 | *8*80 |
| *8*100 | *8*120 | *10*40 | *10*80 | *10*100 | *10*120 | *12*80 | *12*100 | *12*120 | |
| *15*120 | *20*130 | *28*60 | |||||||
Chalco can provide you the most comprehensive inventory of aluminum products and can also supply you customized products. Precise quotation will be provided within 24 hours.
Get a quote